Technology
In This Section
Elements of Urbanaut® Project Costs
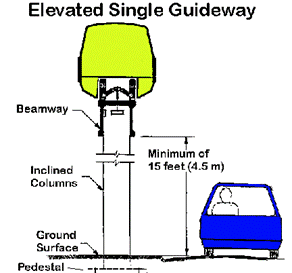
Cost of Type I Single Elevated Guideway
Example of Cost of Type I Guideway
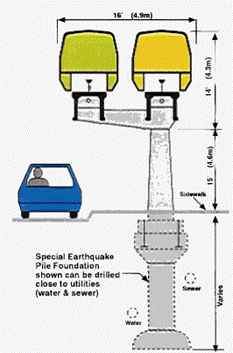
Cost of Type II Dual Elevated Guideway
Cost of Type III Single Guideway at Surface
Comparison of Cost with Other Systems (Link)
Cost of any monorail project is quite involved and varies with the location, the geography and the route layout of the monorail guideway, along with the station location and sizes, service and maintenance facilities, switching and total environmental impact on the community. Urbanaut®has the flexibility to integrate future expansion or deletion, which could reduce planning and construction cost.
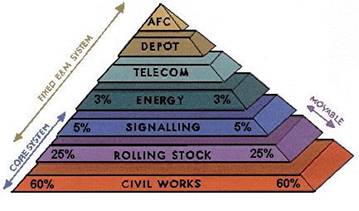
The graphical cost illustration shown in Elements of an Urbanaut®Elevated Monorail Project below is specific to the Urbanaut® technology. While the "Cost Of Depot" is a relatively small item for the Urbanaut®, it is large for the straddle-beam type monorails, which require a very large land area with complicated equipment to move the inseparable massive beam ways with the trains on top.
|
v Civil Works: Guideway, Stations, Switches, Maintenance Buildings v Rolling Stock: Trains and special vehicles v Signaling: Train Control System (TCS) and other controls v Energy: Energy Supply v Telecom: Communication v Depot: Equipment and Control Center v AFC: Automated Fare Collection System |
The "Core System" for the Urbanaut® represents close to 85% of the total project and costs. It embraces:
1. The Civil Works (Elevated Guideway)
2. The Rolling Stock (Vehicles)
3. Signaling (Automatic Control)
The "Fixed E&M" (Electrical & Mechanical) integrates and overlaps with the Civil Works
The "Movable" (Rolling Stock) includes operational trains and vehicles
The following three cost estimate guidelines for an Elevated Single Guideway, Double Guideway and Guideway at Surface are based upon experience on monorail technology by a number of consultants and contractors. A list of variable costs that may apply to any installation is also provided.
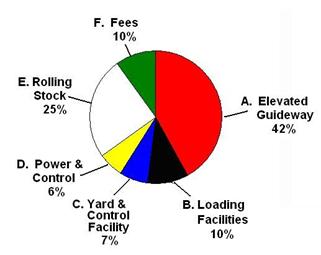
Fixed Costs:
A. Elevated Guideway,
Including Foundations 42%
= $ 6.30 Mill
B. Passenger
Loading / Unloading Facilities (2 Stations) 10% = $
1.50 Mill
C. Maintenance
Yards & Operational Control Facility 7% = $
1.05 Mill
D. Electrical
Power, Signals, and Moving Block Control 6% = $
0.90 Mill
E. Rolling Stock (3
Single Vehicles or 3 Car Train) 25% = $
3.75 Mill
F. Fees &
Contingencies of A, B, C, &
D 10% = $ 1.50 Mill
Total cost of
INTERMEDIATE SIZE PER MILE (1.6 km) 100% = $ 15.00
Mill
|
|
|
|
|
Total miles |
US $ per mile |
% of total cost |
Total |
|
A. |
3.13 miles |
$6.30 million |
42% |
= $19.7 mill |
|
B. |
3.13 miles |
$1.50 million |
10% |
= $4.7 mill |
|
C. |
3.13 miles |
$1.05 million |
7% |
= $3.3 mill |
|
D. |
3.13 miles |
$ .90 million |
6% |
= $2.8 mill |
|
E. |
3.13 miles |
$3.75 million |
25% |
= $11.7 mill |
|
F. |
3.13 miles |
$1.50 million |
10% |
= $4.7 mill |
|
|
|
Total = |
100% |
= $46.9 mill |
Variable cost items to be determined after a preliminary study of the project.
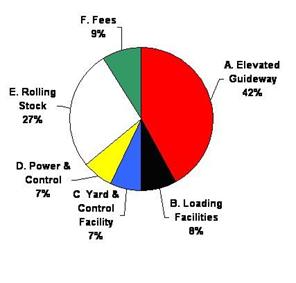
Fixed Costs:
A. Elevated Guideway, Including Foundations 41.8% = $11.70 Mill
B. Passenger Loading / Unloading Facilities (2 Stations) 8.5% = $2.40 Mill
C. Maintenance Yards & Operational Control Facility 7.2% = $2.00 Mill
D. Electrical Power, Signals, and Moving Block Control 7.2% = $2.00 Mill
E. Rolling Stock (3 Single Vehicles or 3 Car Train) 26.8% = $7.50 Mill
F. Fees & Contingencies of A, B, C, & D 8.5% = $2.40 Mill
Total cost of INTERMEDIATE SIZE PER MILE (1.6 km) 100% = $28.0 Mill
|
|
|
Fixed Costs:
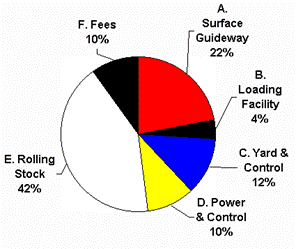
A. Excavation, drainage, sub-ballast,
foundation' 22% = $2.00 Mill
slab, guide rail
B. Passenger Loading / Unloading Facilities (2 Stations) 4% = $0.40 Mill
C. Maintenance Yards & Operational Control Facility 12% = $1.05 Mill
D. Electrical Power, Signals, and Moving Block Control 10% = $0.90 Mill
E. Rolling Stock (3 Single Vehicles or 3 Car Train) 42% = $3.75 Mill
F. Fees & Contingencies of A, B, C, & D 10% = $0.90 Mill
Total cost of INTERMEDIATE SIZE PER MILE (1.6 km) 100% = $9.00 Mill
|
|
|
1. Land acquisition (if necessary public right-of-way not available)
2. Improvements such as relocation of underground and aerial utilities
3. Aerial right-of-way and underground expropriation
4. Parking lots, park-ride facilities
5. Stations built into existing facilities (buildings)
6. Foundations for poor soil conditions and unforeseen underground conditions
7. Special elevated structures that deviate from standard prefabricated designs
8. Legal fees and feasibility studies
9. Unexpected delays and obstructions encountered
10. Financing, interest and loan costs
11. Mobilization costs (Contracts for Design, Engineering, Built proposal)